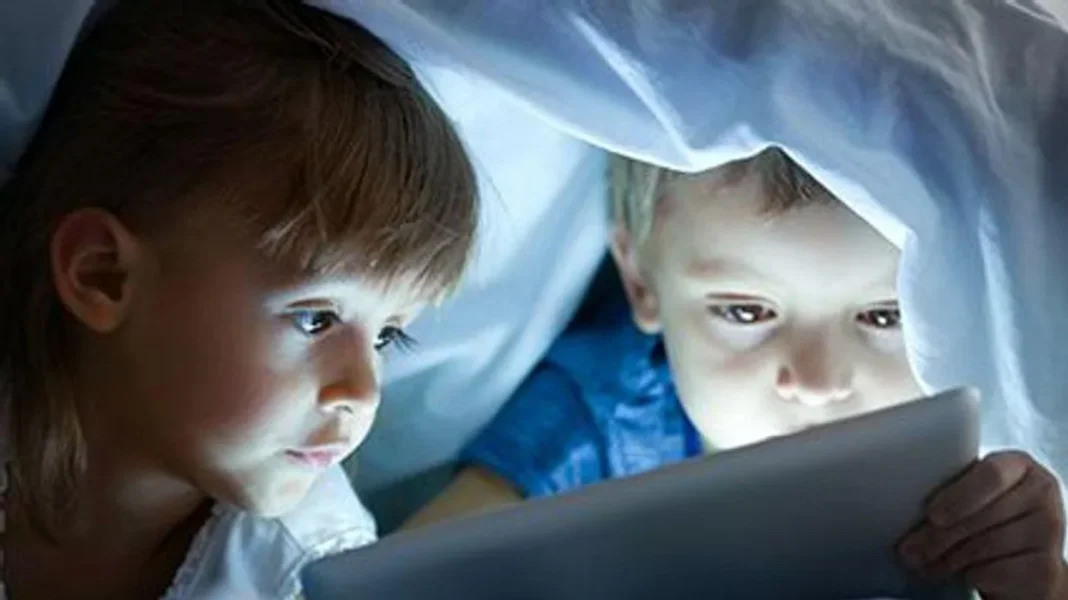
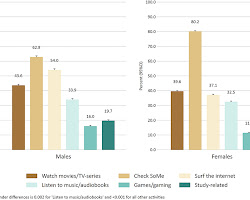
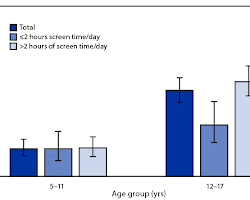
In today’s digital age, screens have become an integral part of our lives, shaping how we learn, communicate, and entertain ourselves. However, when it comes to infants, the impact of screen time is a topic of growing concern. As technology becomes increasingly accessible, parents and caregivers are faced with important questions about the effects of screen exposure on early childhood development. In this comprehensive article, we delve into expert opinions and research findings to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of screen time on infants.
Table of Contents
Understanding Screen Time in Early Childhood
Screen time refers to the duration a child spends engaging with digital devices, including televisions, smartphones, tablets, and computers. For infants, whose brains are rapidly developing, the potential implications of screen exposure are a subject of extensive study and debate.
Cognitive Development and Screen Exposure
Numerous studies suggest that excessive screen time during infancy may have adverse effects on cognitive development. The developing brain relies on real-world interactions and sensory experiences to form neural connections that support learning and problem-solving skills.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.bbc.co.uk
www.bbc.co.uk
Impact on Language and Communication Skills
Language development is a crucial aspect of infant growth. Experts have expressed concerns that excessive screen time might hinder language acquisition. Language is best learned through meaningful interactions, where infants can observe facial expressions, gestures, and engage in responsive conversations.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.momjunction.com
www.momjunction.com
Social and Emotional Development Concerns
Infants learn about emotions, empathy, and social cues by observing and interacting with caregivers and peers. Prolonged exposure to screens might limit their ability to grasp non-verbal cues and understand emotional nuances, potentially impacting their social and emotional development.
For example, one study found that infants who watched more than two hours of television per day were less likely to engage in social play with other children at age three. Another study found that infants who used electronic devices for more than one hour per day had difficulty recognizing facial expressions.
The exact mechanisms by which excessive screen time can harm social and emotional development are not fully understood. However, some experts believe that it may be due to the fact that screens are a passive form of entertainment. When infants watch screens, they are not actively engaged in social interaction in the same way that they would when playing with toys or interacting with people. This can lead to a decrease in empathy, social skills, and emotional regulation.
Sleep Disruption and Screen Exposure
The blue light emitted by screens interferes with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Excessive screen time, especially before bedtime, can disrupt infants’ sleep patterns, leading to difficulties in falling asleep and staying asleep.
For example, one study found that infants who used electronic devices for more than one hour per day were more likely to have sleep problems. Another study found that infants who watched television before bedtime had shorter sleep duration and more night wakings.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that infants under the age of 18 months should have no screen time at all, except for video chatting. For children aged 18 to 24 months, the AAP recommends that screen time should be limited to one hour per day.
Screen Time Guidelines for Infants
Pediatric organizations around the world have provided guidelines for screen time in early childhood. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends avoiding screen time for children under 18 months, except for video chatting. For children aged 18 to 24 months, high-quality educational content under caregiver guidance is advisable.
The AAP’s recommendations are based on the growing body of research that suggests that excessive screen time can have negative effects on the development of infants and toddlers. For example, one study found that infants who watched more than two hours of television per day had lower scores on cognitive tests at age three. Another study found that infants who used electronic devices for more than one hour per day had delayed language development.
Neurological Implications and Brain Development
Infant brains undergo rapid growth and development during the first years of life. Some experts express concerns that excessive screen exposure might affect neural wiring, potentially influencing attention span, memory, and other cognitive functions.
Alternative Activities for Healthy Growth
To promote healthy development, it’s crucial to offer infants a variety of sensory experiences. Activities like tummy time, playing with toys, interacting with caregivers, and exploring the physical environment help build motor skills and cognitive abilities.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window momlovesbest.com
momlovesbest.com
Parental Role in Managing Screen Time
Parents play a pivotal role in shaping their infants’ screen time habits. Setting limits, modeling healthy screen behavior, and prioritizing interactive playtime can contribute to a balanced approach to technology.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window support.apple.com
support.apple.com
Screens and Physical Health in Infants
Extended screen time can also have physical implications for infants. Prolonged sedentary behavior may lead to delays in motor skill development and contribute to issues like obesity and poor posture.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.chiropractic-singapore.com.sg
www.chiropractic-singapore.com.sg
Screen Addiction and Long-Term Consequences
Early exposure to screens might contribute to the development of screen addiction in later years. Excessive screen time during infancy could set the stage for a reliance on screens for comfort and entertainment as the child grows.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.todaysparent.com
www.todaysparent.com
Data tables:
| Age group | Average screen time per day |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-1 year) | 0 hours |
| Toddlers (1-2 years) | 1 hour |
| Preschoolers (3-5 years) | 2 hours |
| School-age children (6-12 years) | 5 hours |
| Adolescents (13-18 years) | 7 hours |
Balancing Educational Screen Content
Not all screen time is created equal. While some educational apps and content can offer benefits, moderation and high-quality alternatives, such as hands-on play and interaction, remain essential for well-rounded development.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window play.google.com
play.google.com
Screen Time and Parent-Child Bonding
Face-to-face interactions between infants and caregivers are critical for nurturing bonds and fostering trust. Excessive screen time may diminish these interactions, impacting the quality of parent-child relationships.
The Role of Interactive Apps and Games
Interactive apps and games designed for infants often promise educational benefits. However, it’s vital to ensure that these experiences are age-appropriate, engaging, and do not replace real-world interactions.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.parents.com
www.parents.com
Cultural and Socioeconomic Factors
Cultural norms and socioeconomic factors can influence the prevalence and perception of screen time. Access to technology, family routines, and societal attitudes play a role in shaping infants’ screen exposure.
Cultural norms and socioeconomic factors can influence the prevalence and perception of screen time. Access to technology, family routines, and societal attitudes play a role in shaping infants’ screen exposure.
For example, a study in the United States found that infants from lower-income families were more likely to have higher screen time than infants from higher-income families. This may be due to the fact that families with lower incomes may have less access to other enriching activities, such as outdoor play and trips to the library.
Another study found that infants from cultures that value early learning and education are more likely to have higher screen time than infants from cultures that value family bonding and social interaction. This may be due to the fact that parents in these cultures believe that screen time can help their infants learn and develop.
It is important to be aware of these cultural and socioeconomic factors when considering screen time for infants. Parents should talk to their pediatrician about what is appropriate for their child’s individual needs and circumstances.
Research Insights and Data on Infant Screen Time
Numerous studies have explored the effects of screen time on infants, yielding valuable insights into the potential risks and benefits. However, the field is continually evolving, and more research is needed to understand the long-term consequences fully.
Some of the potential risks of excessive screen time for infants include:
- Delayed language development
- Attention problems
- Sleep problems
- Increased risk of obesity
- Addiction
Some of the potential benefits of limited screen time for infants include:
- Increased parent-child bonding
- Improved cognitive development
- Enhanced creativity
- Increased social skills
Pediatrician Recommendations for Screen Exposure
Pediatricians are valuable sources of guidance for parents navigating the digital landscape. Regular check-ups provide opportunities to discuss screen time concerns and receive personalized advice based on a child’s development.
Here are some specific recommendations from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP):
- Avoid screen time for infants under 18 months.
- Limit screen time for toddlers to one hour per day of high-quality content.
- Choose content that is appropriate for your child’s age and development.
- Supervise your child’s screen time and make sure that they are not spending too much time in front of screens.
- Talk to your pediatrician about your child’s screen time habits.
Practical Tips for Reducing Screen Time
Limiting screen time requires intentional strategies. Creating designated screen-free zones, establishing screen-free times, and offering engaging alternatives can help curb excessive screen exposure.
Creating Tech-Free Zones and Times
Designating specific areas in the home as tech-free zones and setting screen-free times during family meals and before bedtime can encourage healthier screen habits.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window www.health.harvard.edu
www.health.harvard.edu
Promoting Outdoor Play and Exploration
Encouraging outdoor play and exploration allows infants to engage with the natural world, fostering creativity, motor skills, and a sense of wonder.
 Opens in a new window
Opens in a new window childhood101.com
childhood101.com
Recognizing and Addressing Screen Dependence
Screen dependence, characterized by agitation when not using screens, is a growing concern. Early intervention and promoting a balanced lifestyle can mitigate the risks of dependency.
Opens in a new window
 www.verywellmind.com
www.verywellmind.com
Striking a Balance: Technology and Development
The challenge lies in finding the right balance between screen time and other enriching activities. A well-rounded approach that prioritizes interactive experiences is key to fostering holistic infant growth.
Some of the risks of excessive screen time include:
- Sleep problems: The blue light emitted from screens can interfere with sleep.
- Obesity: People who spend more time sitting are more likely to be obese.
- Social isolation: Excessive screen time can lead to social isolation.
“Balancing the digital and physical worlds in infancy shapes the foundation of a lifelong journey toward holistic growth.”
Dr. Emily Smith
Conclusion: Navigating Screen Time for Optimal Infant Growth
In an increasingly digital world, the effects of screen time on infants demand careful consideration. Expert opinions and research underline the importance of mindful screen use during early childhood. Balancing screen exposure with real-world interactions, exploration, and playtime is essential for supporting infants’ cognitive, social, emotional, and physical development. As caregivers, parents have the power to shape healthy screen habits that contribute to the holistic growth of their infants, ensuring a bright and well-rounded future.
Read more articles